Epoxy colors: which dyes are available and which ones do you choose and when?
Do you want epoxy colors with a sleek result? Then choosing the right dye is more important than many makers think. Not every dye behaves the same in resin: some give a transparent glass effect, others make your work completely opaque, and some provide special effects such as petri-dish or glow.
In this article you will find a practical overview of the most commonly used colorants for epoxy, including when to use them, what the differences are and how to add them correctly.
Best choice per project (quick choice)
| Project | What did I use? | Why |
|---|---|---|
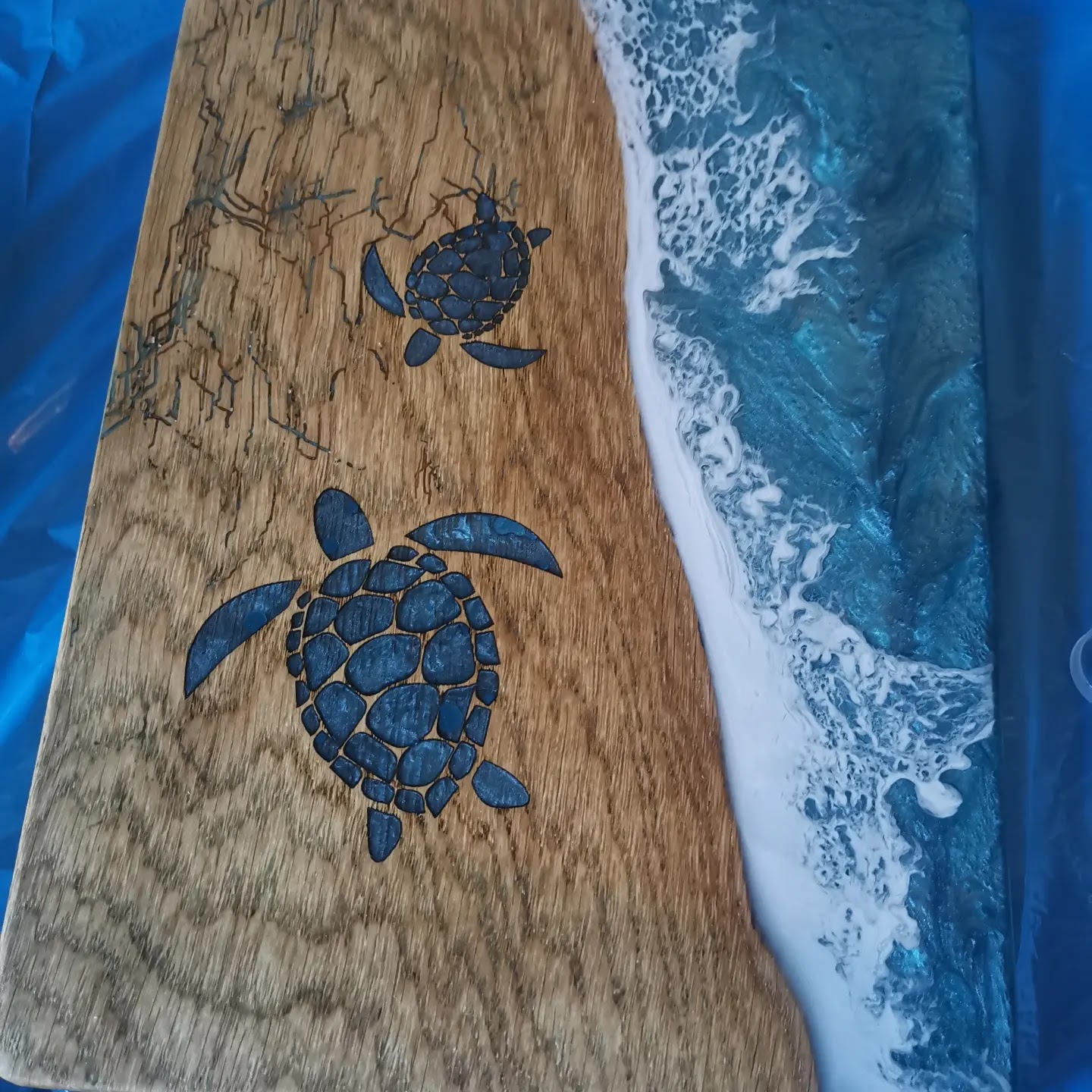 Tapas board / serving board | Mica powder + a little pigment paste | Metallic depth, luxurious look, good coverage |
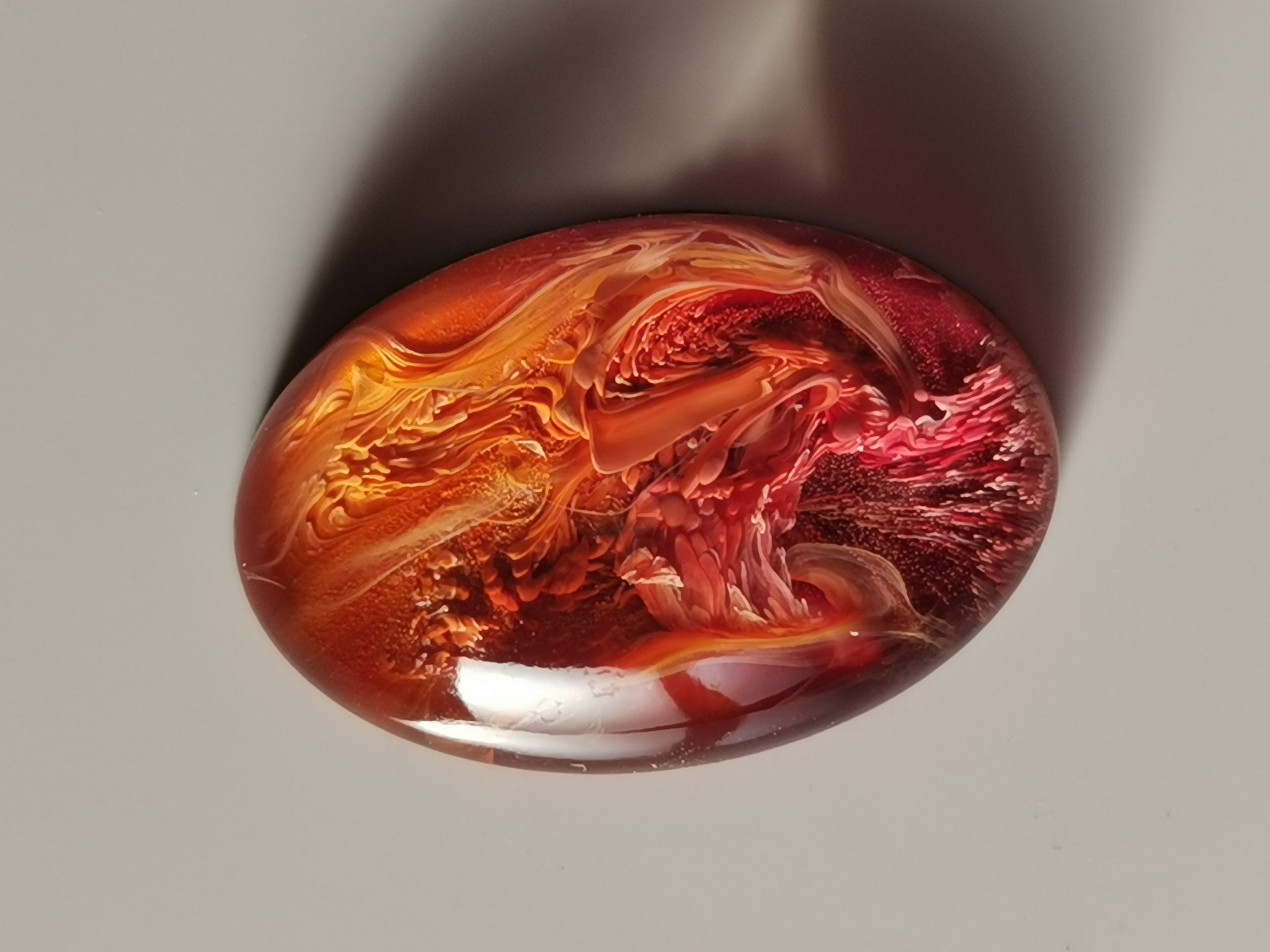 Petri jewelry or coasters in mold | Alcohol ink + deep white sinker | Sinking lines and organic depth |
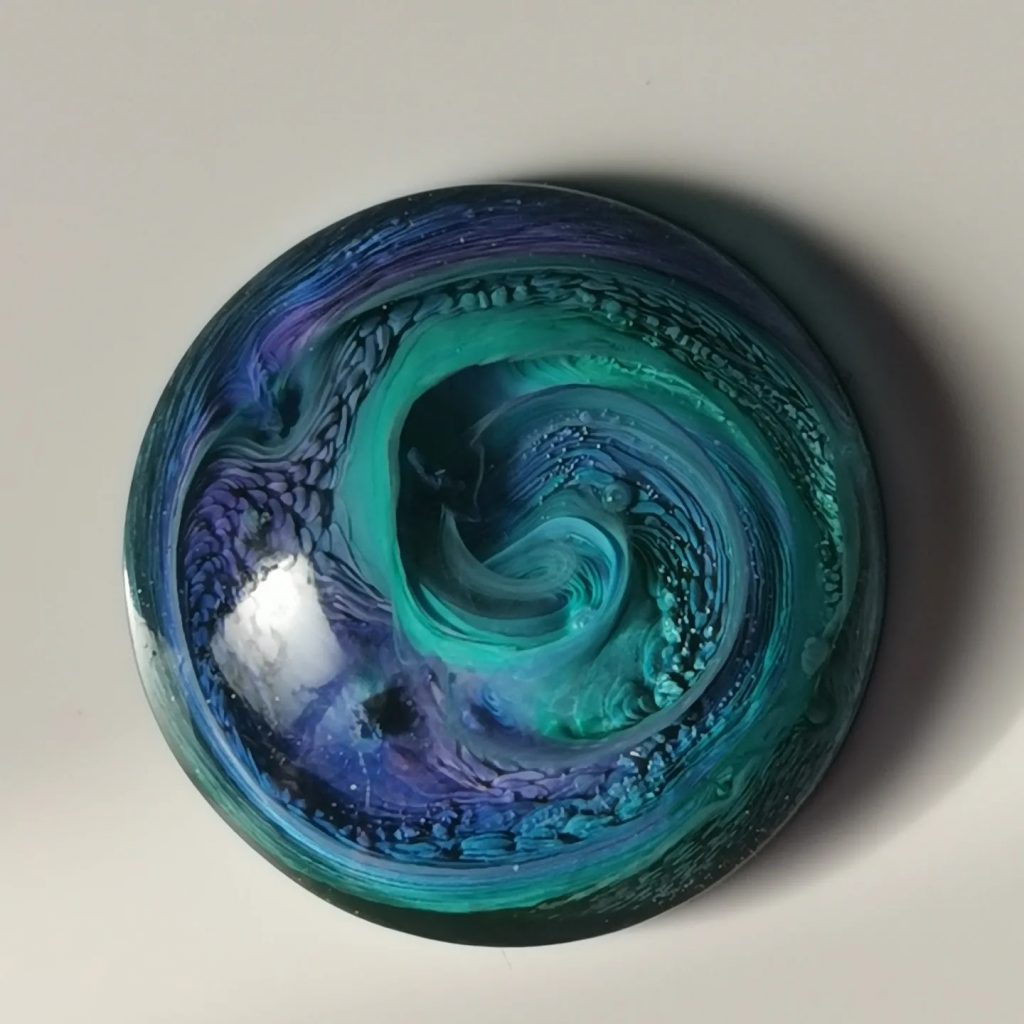
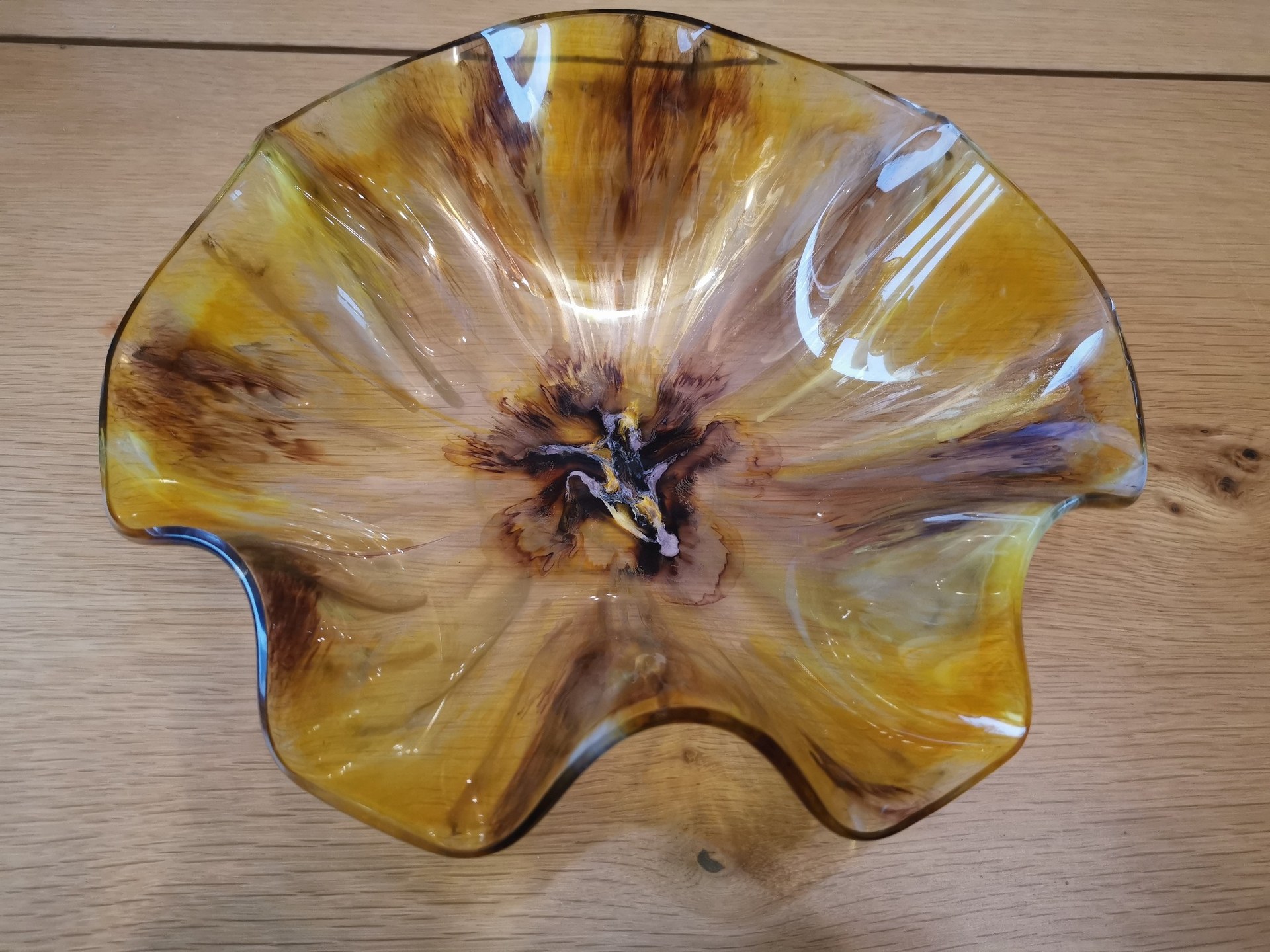 Transparent ornamental objects | Liquid resin dyes or alcohol inks (I used alcohol inks for this bowl) | Clear, translucent, glass look |
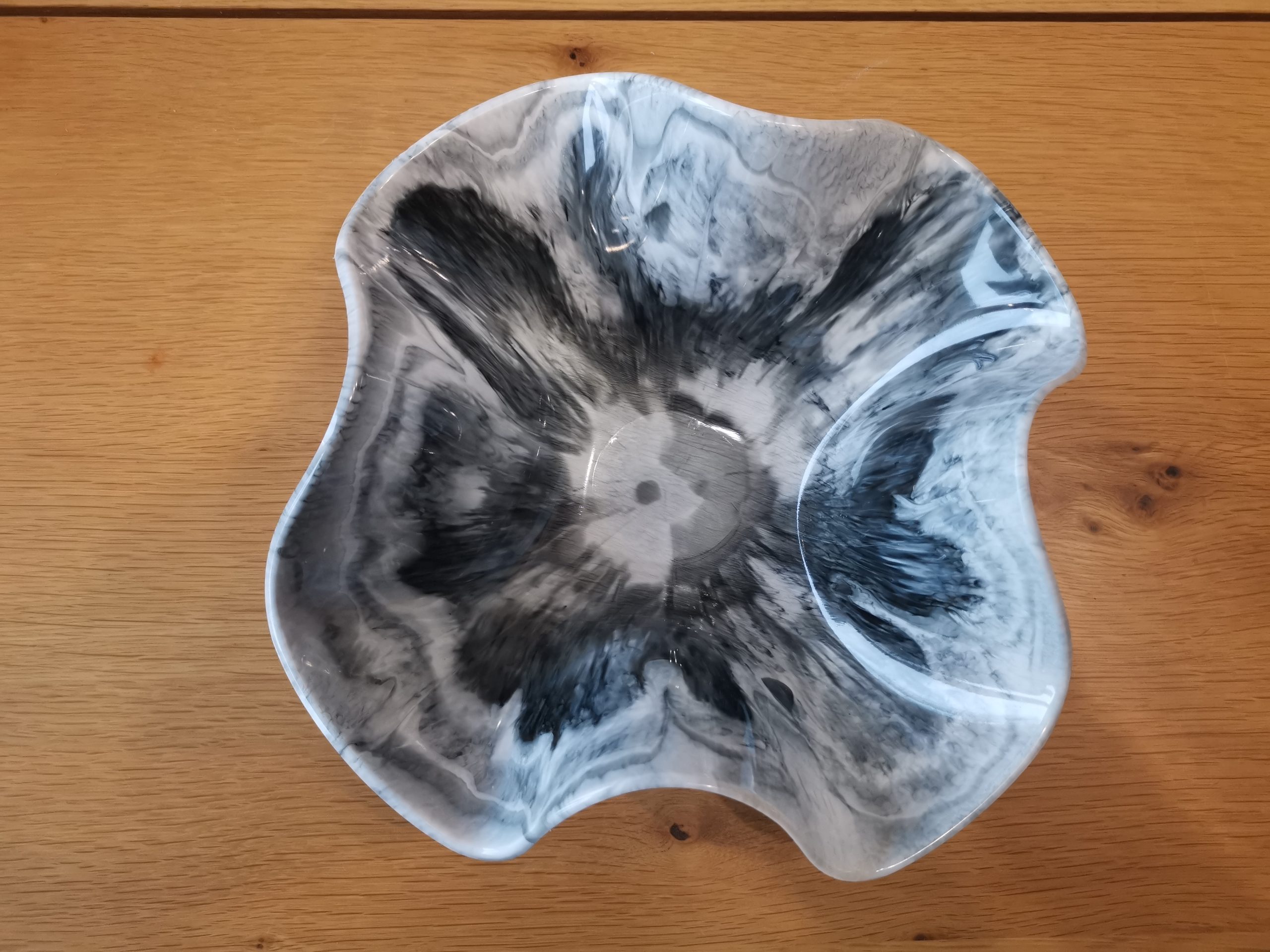 Sleek, even color areas | Epoxy pigment paste and black alcohol ink | Powerful opaque color with little product |
| Statement piece with glow or flip effect | Glow/chameleon pigments | Light-in-the-dark or color shift effects |
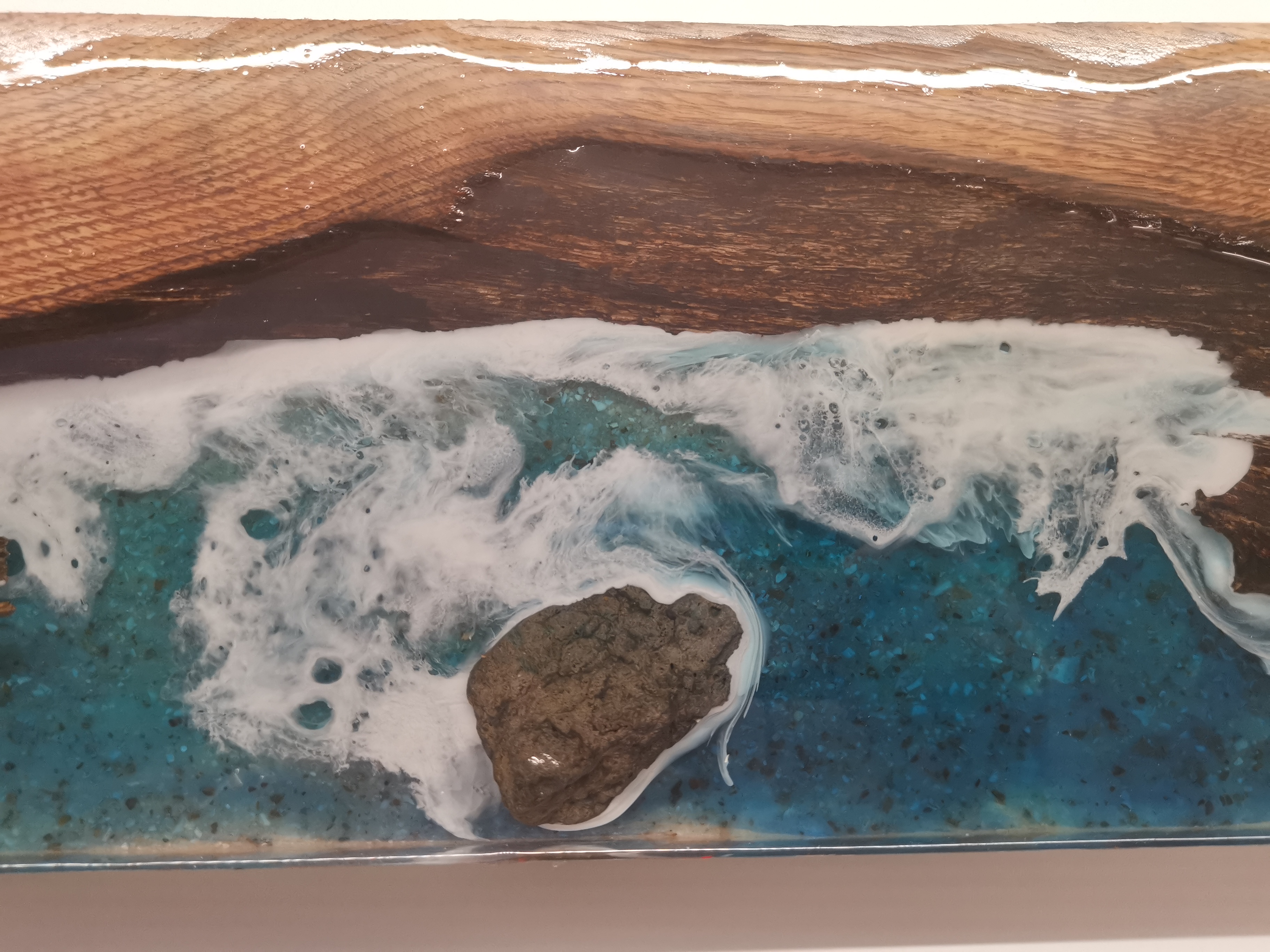 Ocean art panels, beach coasters (opaque white) | Ocean waves white / wave white | Lacing, foam heads and cells |
My own experience: I use this myself
For mytapas boardsI mainly usemica powderwhen I want an opaque metallic effect with depth and shine. Forpetri dish effectsI work withalcohol inks + deep white sinker. I also useepoxy pigmentswhen I need smooth, full opaque colors.
Those are three strong choices, but there are other dyes that can perform better in specific projects. Below I put them all clearly next to each other.
Overview: types of dyes for epoxy
NB:the brand names below are a practical shortlist of commonly used options, not an absolute top or best brand list. End result depends on resin, dosage and technique. Always test new combinations on a small scale first.
| Dye | Effect + transparency | Best for | Where to buy |
|---|---|---|---|
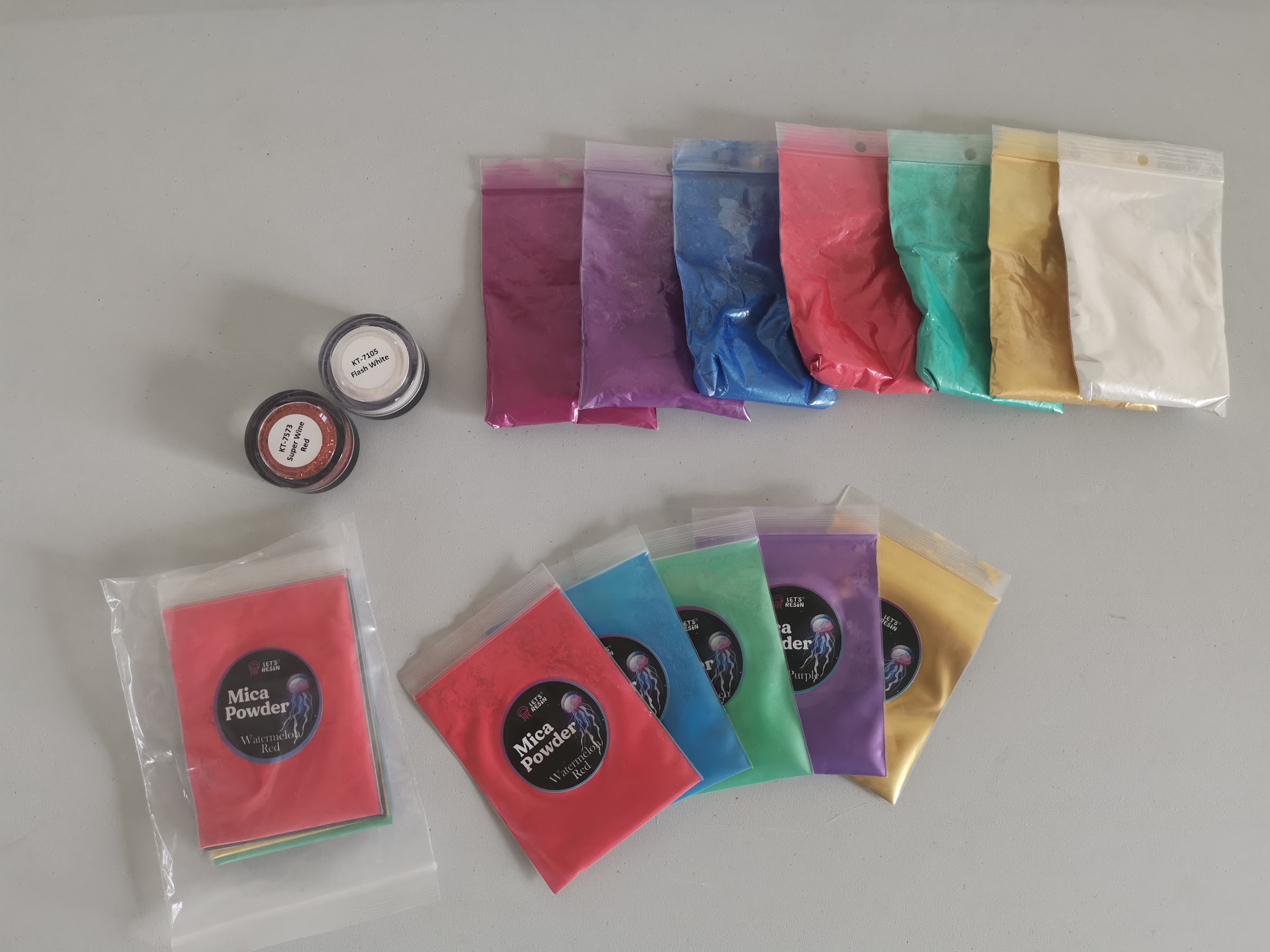 Mica powder | Mother of pearl/metallic shimmer Transparency: semi-opaque to opaque | Decorative objects, tapas boards, jewelry, everything except petri, waves and glass look | Letsresin |
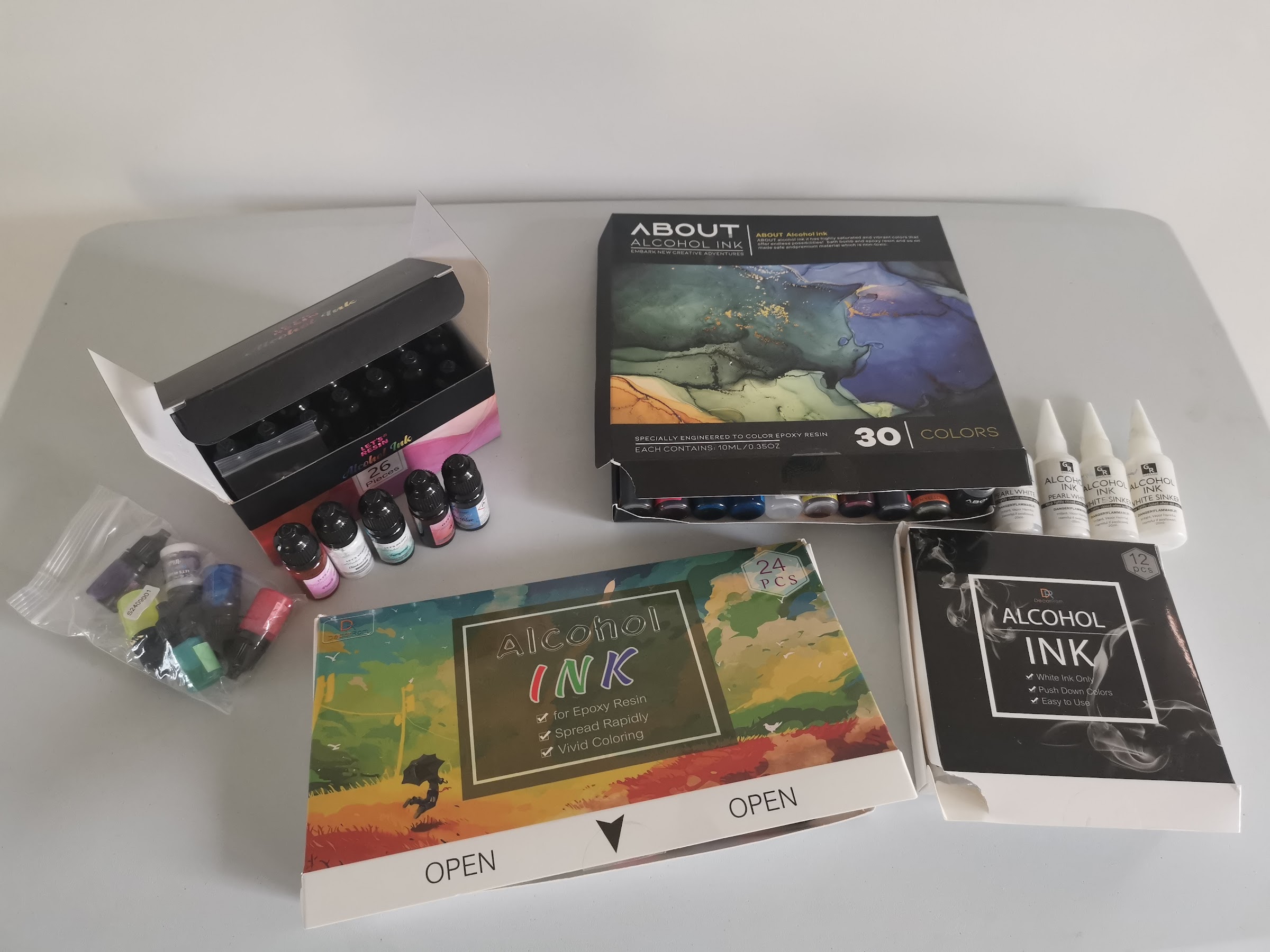 Alcohol ink | Inky flow, organic patterns Transparency: transparent | Petri and transparent colors of resin | Letsresin DecorRom |
 White sinker (alcohol ink white) | Pushes color down in layers Transparency: opaque white | Petri dish effect | DecorRom |
 Epoxy pigment paste | Even, highly opaque Transparency: opaque | Tables, trays, coasters, blocks, anything that needs an opaque solid color | Ocean Ocean2 |
 Liquid resin dyes | Clear color without glitter Transparency: transparent to semi-transparent | Transparent castings, layers, glass look. Not suitable for PETRI-ART | Pigment |
 Glow powder and chameleon powder | Glows in the dark and creates a color-shift effect Transparency: usually semi-opaque | Decor, art pieces, similar use as mica powder | AliExpress/Temu |
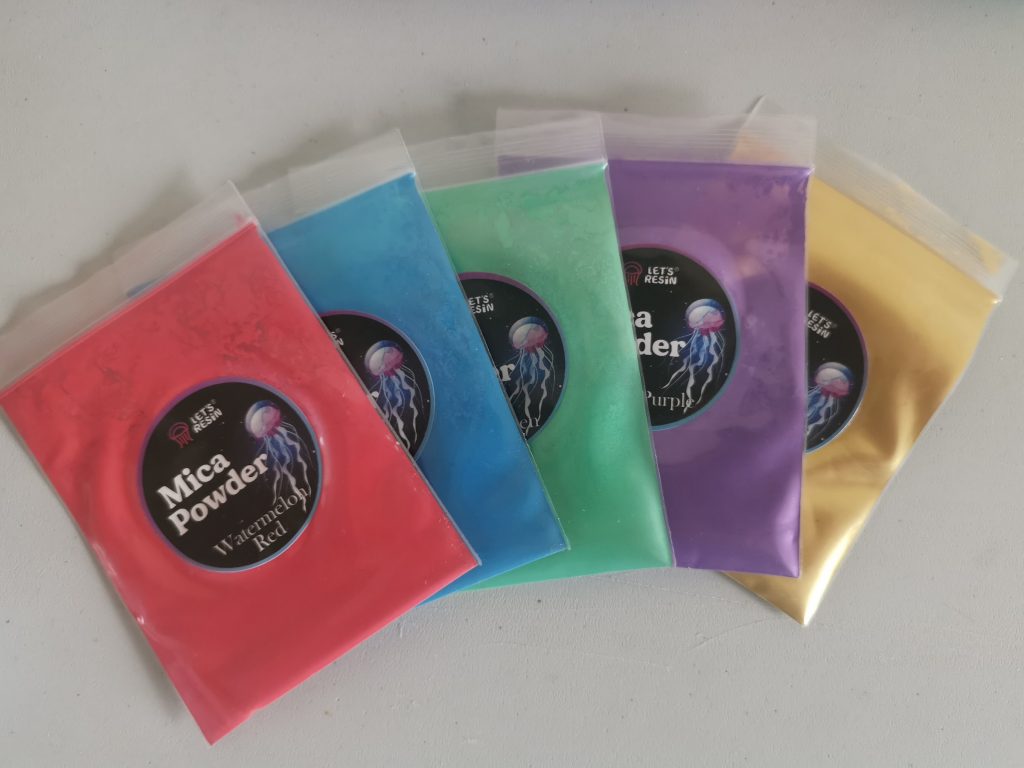
1) Mica powder

Commonly used brands for mica powder:Let’s Resin, Alumilite (PolyColor), Stone Coat (PolyColor), ArtResin (mica-compatible workflows). In my opinion you can’t do much harm with cheaper powders. Be careful when using this on objects that come into contact with food. Make sure everything is food safe.
What does it do?
Mica gives a shiny, metallic or pearly effect. Perfect if you want depth and a luxurious look.
What is best used for?
Decorative objects, tapas boards, jewelry, everything except petri, waves and glass look
Difference with other dyes:
Mica givesgloss particles, not a “pure flat color” like pigment paste.
How to use mica correctly:
- First mix resin + hardener completely.
- Add mica in small increments and stir gently until homogeneous.
- Use multiple shades in separate cups for swipe or swirl effects.
You can also rub/color your mold with the mica powder and then pour clear or colored resin into the mold. Then only the outer layer of your object is colored.


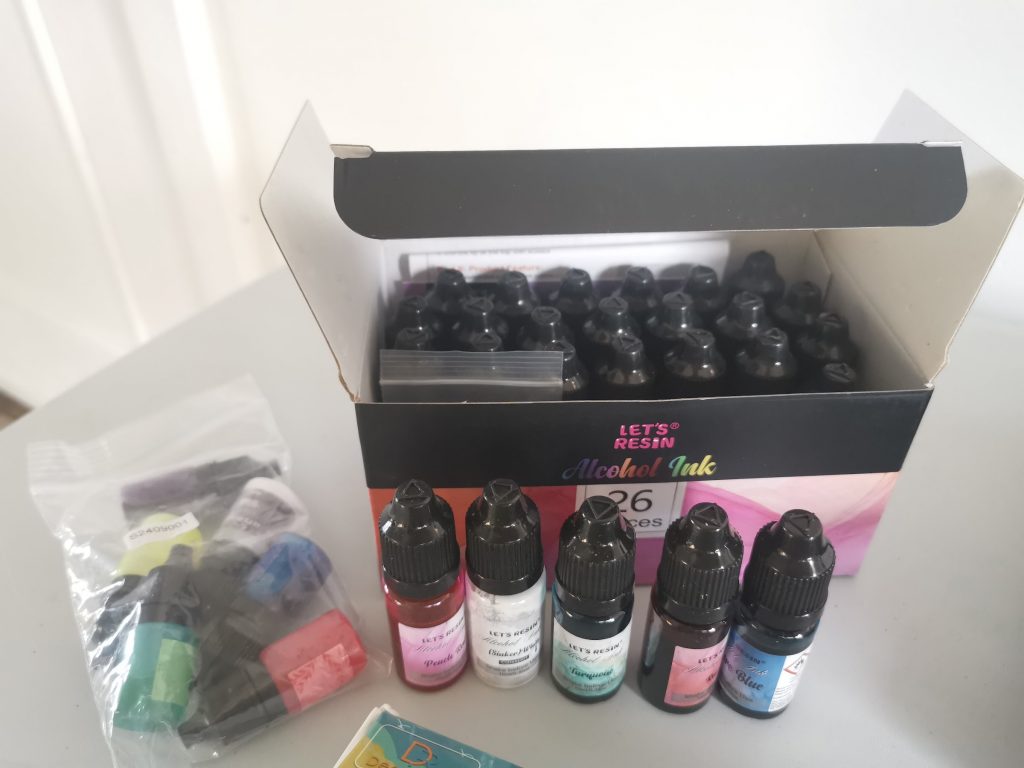
2) Alcohol inks + deep white sinker (petri)

Commonly used brands for alcohol ink (petri/swirl):Let’s Resin, Alumilite Color Creator, Jacquard Piñata.
What does it do?
Alcohol ink spreads quickly and produces transparent, organic layers of color. A white sinker (heavier white alcohol ink) pushes color down and makes the typical petri-dish pattern.
What is best used for?
Petri coasters, small molds, artistic decor pieces, Petri jewelry and transparent colors of resin.
Difference with other dyes:
Alcohol ink is ideal for moving patterns, but less suitable if you want a completely smooth, opaque color area. It remains translucent unless mixed with white sinker ink.
How to use alcohol ink correctly:
- Pour a clear coat of epoxy into the mold.
- Drop drops of color ink.
- Then add 1 drop of white sinker on top of the color to create the “sink”.
- Work in thin layers and test first, as some inks can affect curing if overdosed.



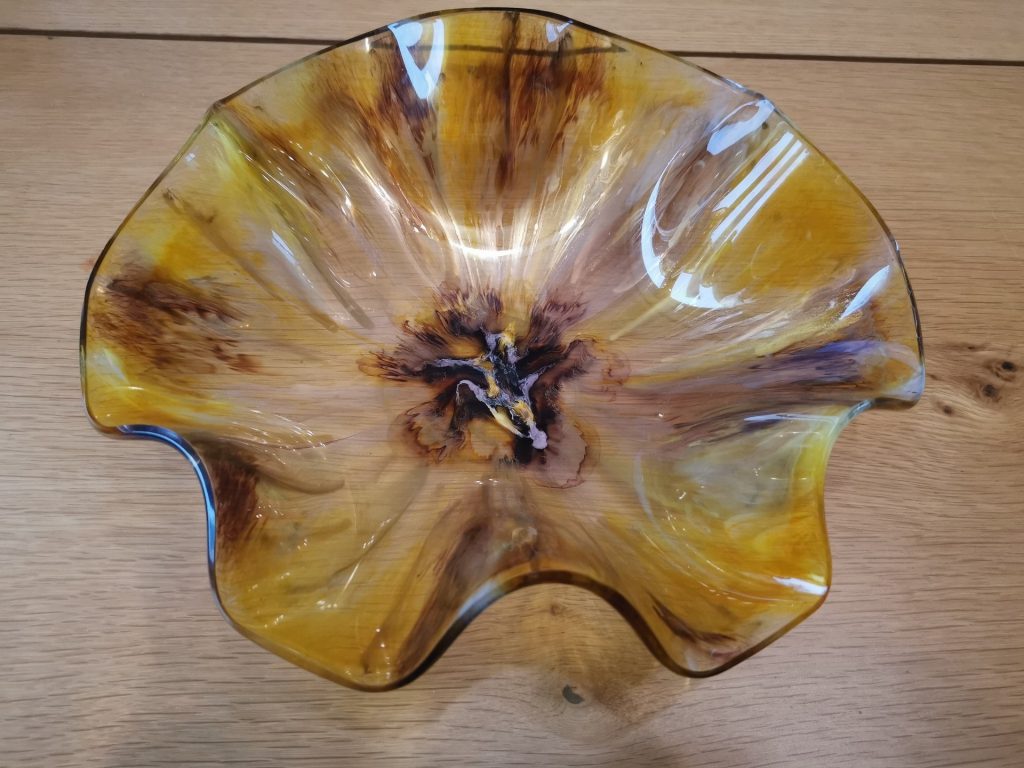
Alcohol ink as transparent color (without petri)
You can also use alcohol inks perfectlyclear, transparent dyein epoxy, comparable to resin dyes. You then useno white sinker. This is ideal if you want to add color but still maintain depth and light transmission.
This is how you use alcohol ink for transparent color:
- First mix epoxy and hardener completely according to the correct ratio.
- Add 1-2 small drops of alcohol ink per mixing cup and stir well.
- Build up color slowly with additional drops until you reach the desired intensity.
- Work in thin layers for a nice “glass” depth and always test new colors on a small scale first.
- Keep the dosage low: overdosing can affect curing.



3) Epoxy pigment paste (opaque colors)
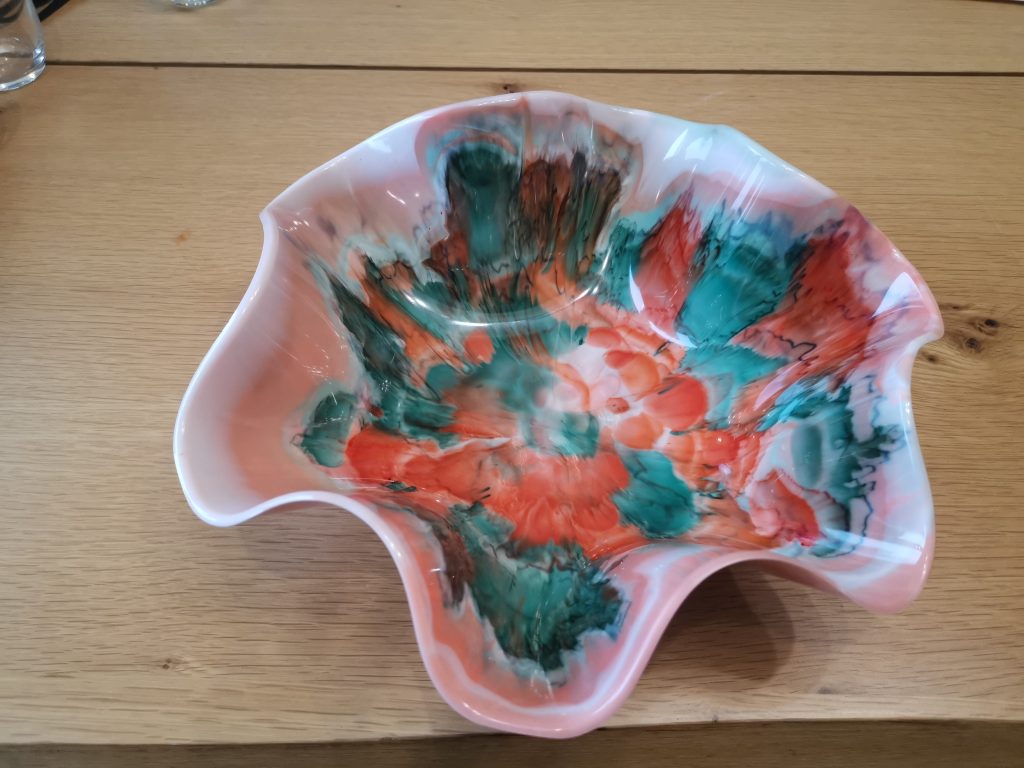

Commonly used brands for opaque pigments/paste:TotalBoat Pigment, Let’s Resin Pigment Paste, MAS pigment, Stone Coat pigment kits.
What does it do?
Pigment paste gives powerful, opaque colors with little product. Ideal for sleek, professional color areas.
What is best used for?
Coasters, table inlays, river details, trays and projects where you don’t want any transparency.
Difference with other dyes:
Pigment paste is the best choice foreven opaque color; mica is more likely to give a shine, while alcohol ink is more likely to produce transparent movement.
This is how you use pigment paste correctly:
- Start with a mini amount (toothpick tip) and build up.
- Stir well to avoid color streaks.
- Do not use more than necessary: too much additive can disrupt the resin balance.
4) Liquid resin dyes (transparent dyes)
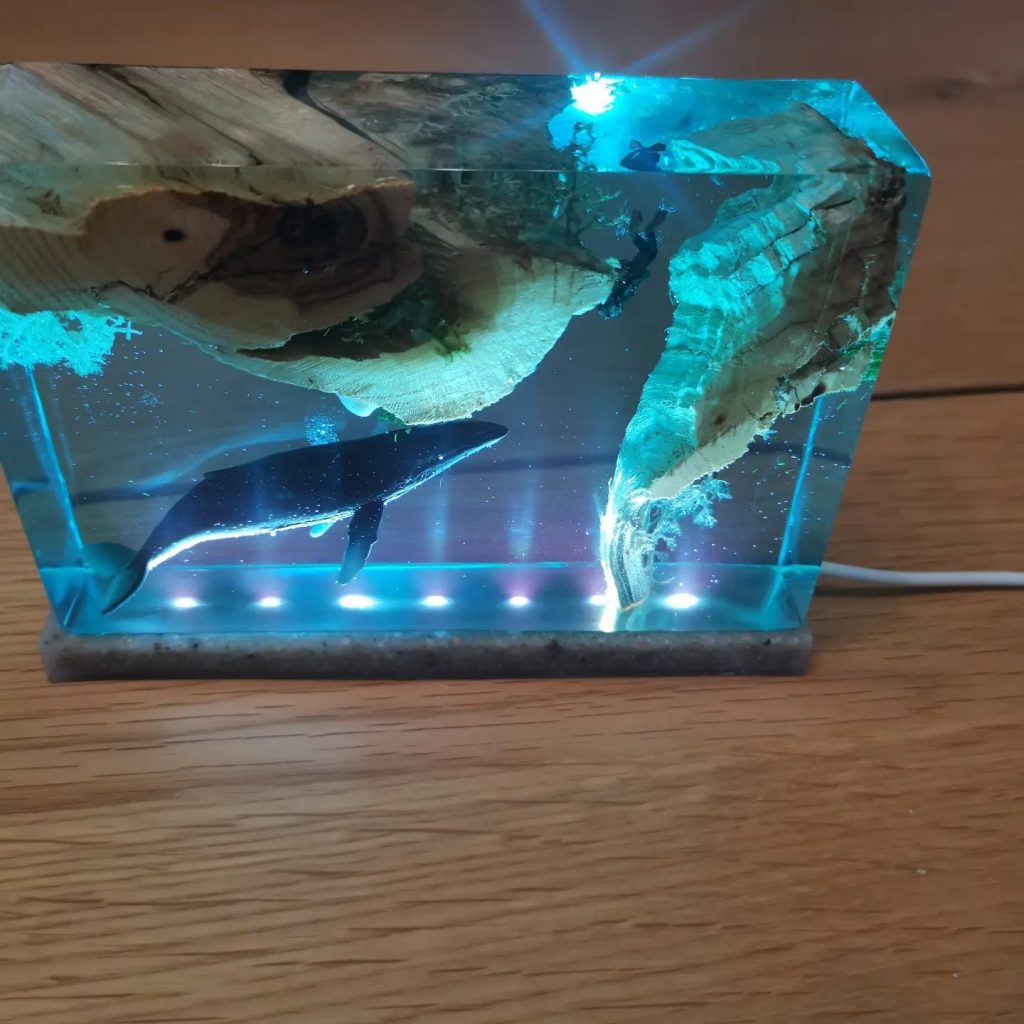

Commonly used brands for transparent liquid shades:ArtResin ResinTint, TotalBoat TotalTint Mixol (always test compatibility first), Alumilite dyes. Always test new combinations on a small scale first.
What does it do?
These dyes provide bright color without metallic sheen. Useful if you want to maintain depth, layers and light transmission. You can also replace this with alcohol inks. That I what I do in most projects.
What is best used for?
Transparent castings, bloom effects, decorative objects with a “glass” look.
Difference with other dyes:
More clear and “clean” than mica; less opaque than pigment paste. You can compare it with alcohol ink.
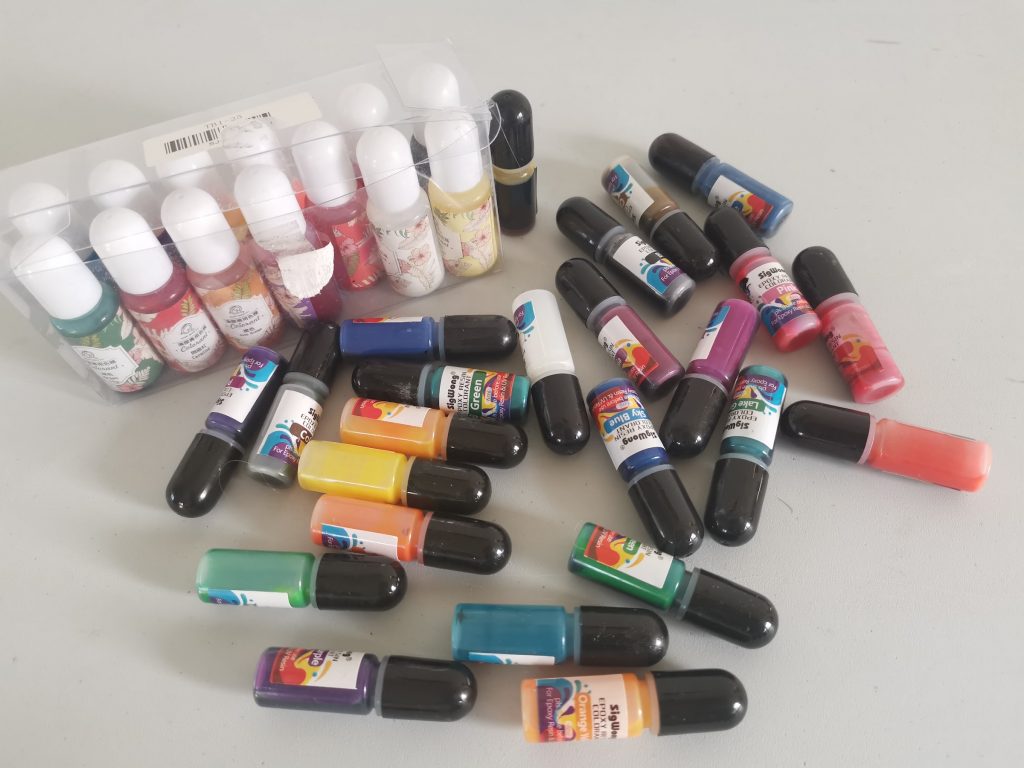

5) Glow powders and effect pigments (chameleon, neon, glitter)
Frequently used brands for glow/effect powders:Alumilite PolyColor Glow and chameleon/effect powders from resin brands. In my opinion you can’t do much harm with cheaper powders. Be careful when using this on objects that come into contact with food. Make sure everything is food safe.
What are they doing?
Glow powders charge with light and glow in the dark. Chameleon and effect pigments change hue depending on viewing angle or light incidence.
What is best to use them for?
Statement pieces, night-effect decor, special designs.
Difference with other dyes:
These are mainlyeffect carriers; If necessary, combine them with a base pigment for better readable color.
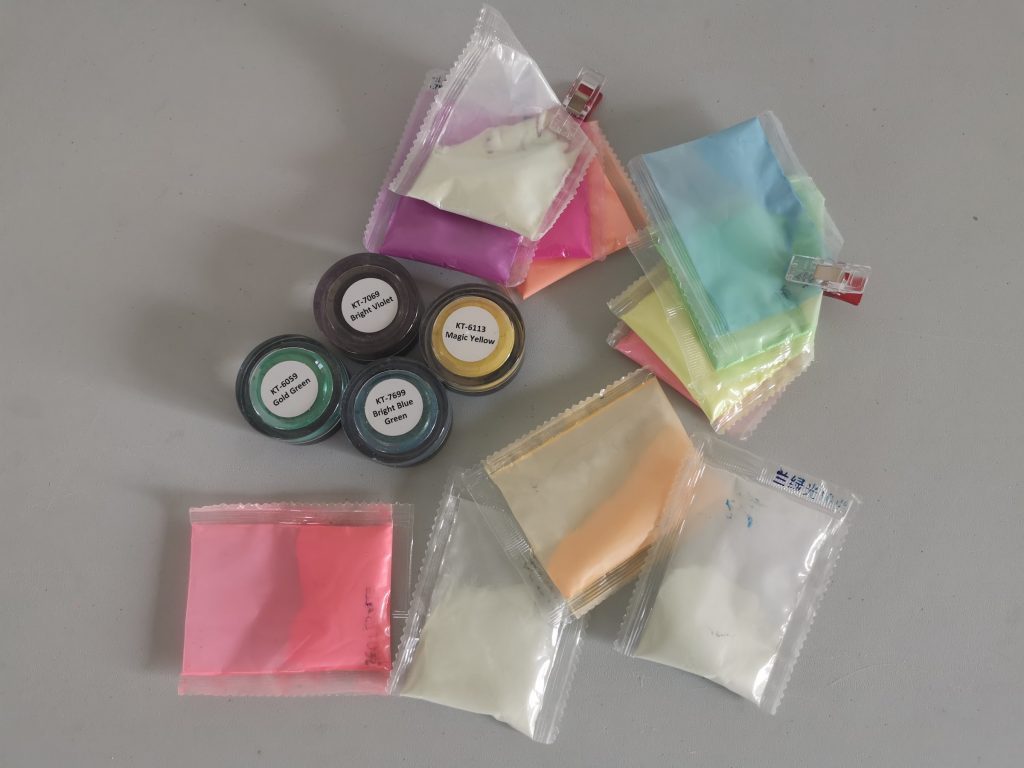

6) Ocean waves white / wave white (lacing)

Commonly used brands for ocean waves white/lacing:MAS Ocean Art White Pigment, Let’s Resin Ocean White Pigment Paste, Artistry Epoxy Wave White.
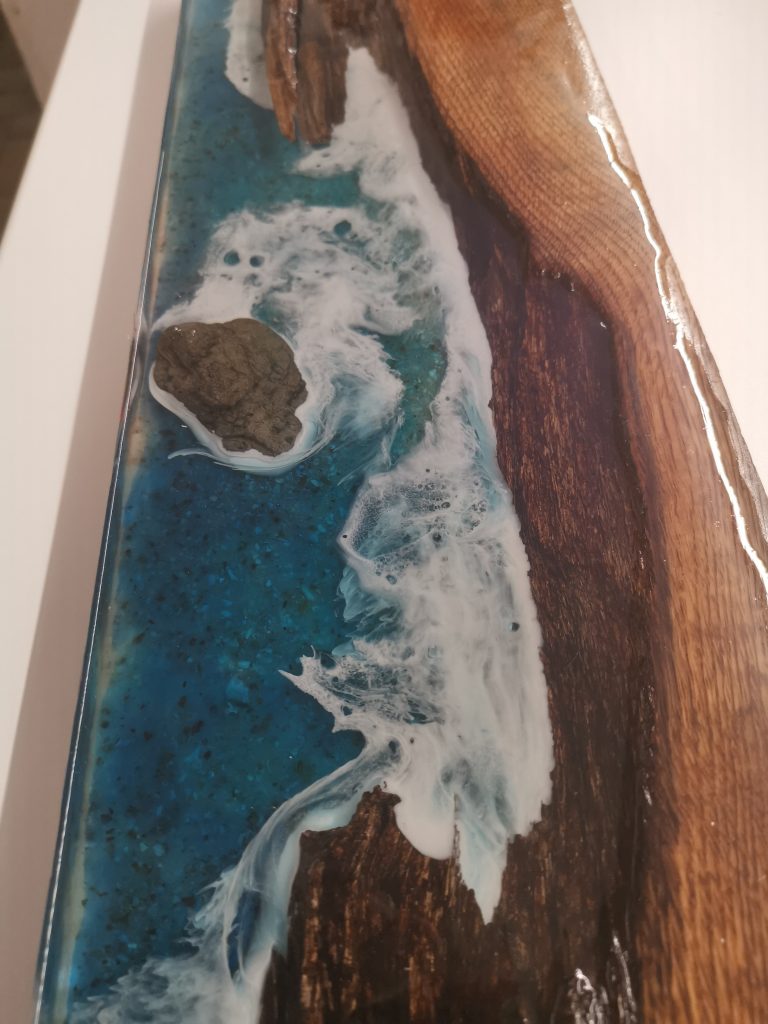
A dye that certainly belongs in the overview isocean waves white(also sold as wave white, ocean white or white pigment paste for lacing). This is not the same as regular white food coloring: these products are designed to be easiercells, foam lines and lacingto form in sea compositions.
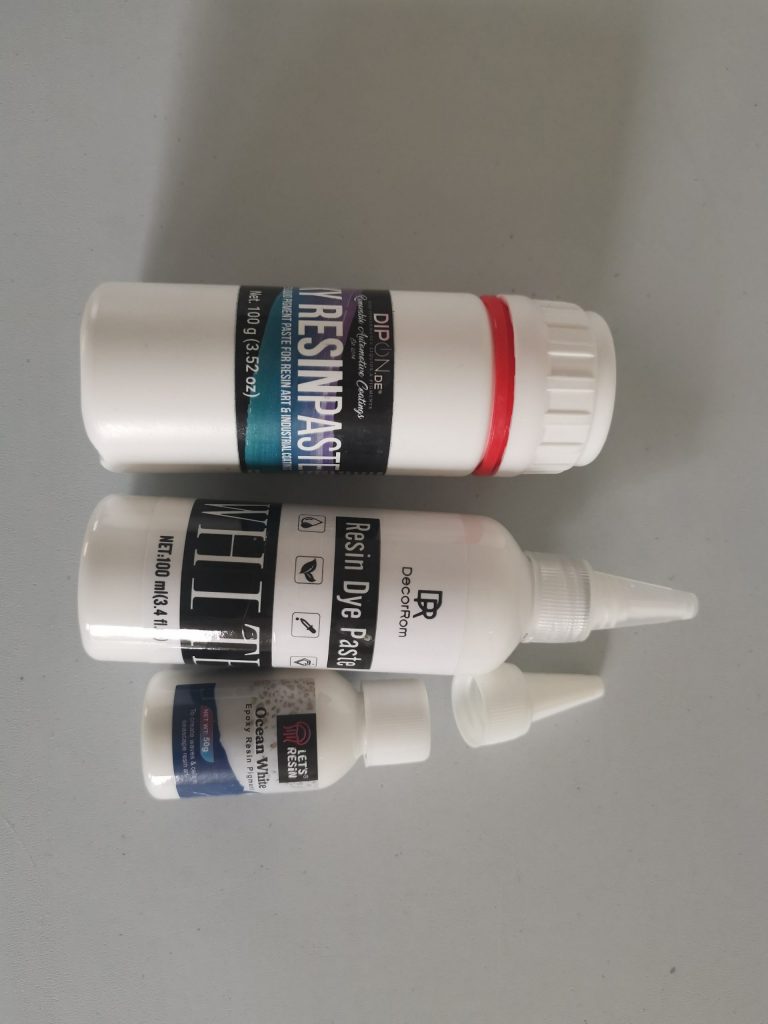

| Dye | Effect | Best use for | Tip |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ocean waves white / white lacing paste | Foaming wave heads, cells and lacing | Ocean art, beach panels, beach coasters | Work on slightly thickened resin and blow out with a heat gun for tighter wave lines. |
| Deep white sinker (alcohol ink) | Sinking petri effect in depth | Petri in molds | Particularly suitable for petri, less so for wide wave lacing on panels. |
Short difference:for petri remains a white sinker top; for ocean waves on panels, a specific ocean/wave white pigment usually works more consistently.
Important: which dyes should be avoided?
- Preferably use dyes that are explicitly intended for epoxy.
- Avoid water-based dyes (such as many watercolors) in epoxy: water can interfere with the reaction.
- Overdose (also with alcohol ink) can negatively affect curing: always test small first.
- For Petri effects: choose a resin that is suitable for this type of technique and follow the product sheet.
What else can you read?
- Which epoxy resin do you need? Comparison per project
- Amine blush with epoxy: prevention and correct removal
Frequently asked questions
Can I use acrylic paint to color epoxy?
This sometimes works in small quantities, but it is less predictable. Epoxy-specific dyes remain the safest choice for consistent cure and color.
Why does my white ink sink down at petri?
That is precisely the purpose of a sinker: the white component is heavier and pulls color downwards, creating the Petri effect. Do you want it not to sink so deep? Then let your resin thicken a bit.
What is the difference between mica and pigment paste?
Mica = shimmer/metallic particles. Pigment paste = opaque, even color without glitter look.
How do I prevent epoxy from not curing properly after coloring?
Use epoxy-compatible dyes, add little, stir well and test new combinations on a small scale first.
In summary:for a metallic opaque look (such as in tapas planks), mica remains top. For petri, choose alcohol ink with white sinker. For tight, full colors, pigment paste is usually the best choice.
